Long ago human
beings dreamed of knowing space, traveling the moon or other planets,
being able to study them more clearly, to be able to see them more
closely, nowadays, with advances in technology, many of these dreams have come true. Get to know some of the most important instruments used in space exploration.
International Space Station: The International Space Station '' (or simply ISS) is a space laboratory currently under construction. The orbiting of the EEI began in 1998 and the station is in a low orbit (between 340 km and 353 km) that makes it possible to be seen from Earth with naked eyes. Traveling at an average speed of 27,700 km / h, the Station completes 15.77 orbits per day. In the continuity of operations of Mir of Russia, Skylab of the United States, and of European Columbus, the International Space Station represents the human permanence in the space and has been maintained with crews of no less than two elements since 2 November 2000. At each crew surrender, the station comprises both teams (in progress and the next), as well as one or more visitors.
Insignia of the International Space Station: Space Suits:
Autonomous robots are robots that can accomplish the desired goals in unstructured environments without human help. A
high level of autonomy is particularly desired in fields such as space
exploration, where communication has delays and interruptions are
inevitable.
In 1997 NASA sent its Mars Rover Explorer, Mars Path Finder, to Mars to investigate the geology and morphology of that planet's surface, and hundreds of meters below ground, geochemistry and soil and petrology. of the rocks, the magnetic properties of the soil, such as the magnetic properties of dust.
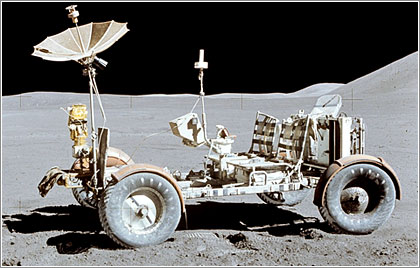
Vehicle Explorer of the Moon:
The Lunar Rover is a
small electric vehicle that allowed Apollo astronauts to drive in the
vicinity of the landing site of the lunar module, to conduct geological
observations, to collect samples of rocks and desolos, to make use of scientific instruments, at various points on the Moon.
The vehicle was first used on the Apollo 15 mission and was the fourth landing of the Apollo mission on the moon. The vehicle was used to explore distant regions about 5 km from the landing site. The vehicle was also used on the Apollo 16 and Apollo 17 missions.
Observatories:
An Observatory is the
place used for observations and studies of terrestrial and celestial
events used by various sciences: astronomy, climatology, geology,
meteorology, oceanography and volcanology. The most well-known type is the astronomical one that uses the telescope to peer into the skies, usually at night.International Space Station: The International Space Station '' (or simply ISS) is a space laboratory currently under construction. The orbiting of the EEI began in 1998 and the station is in a low orbit (between 340 km and 353 km) that makes it possible to be seen from Earth with naked eyes. Traveling at an average speed of 27,700 km / h, the Station completes 15.77 orbits per day. In the continuity of operations of Mir of Russia, Skylab of the United States, and of European Columbus, the International Space Station represents the human permanence in the space and has been maintained with crews of no less than two elements since 2 November 2000. At each crew surrender, the station comprises both teams (in progress and the next), as well as one or more visitors.
Insignia of the International Space Station: Space Suits:
The space suit is a
complex system of clothing, equipment and environmental systems designed
to keep a person alive and comfortable in the difficult environment of
outer space. This applies to extraveular activities (EVA) outside a spacecraft orbiting the Earth and walking on the surface of the Moon.
The man has always
observed the stars, but only after the invention of the telescope, it
was possible to enlarge the images of the celestial objects. There are three types of telescope: Reflectors, refractors and radio telescopes. Reflectors and refractors are optical telescopes: they collect and amplify visible light. Reflectors use mirrors to collect light from light and refractors use lenses. Raditelescopes
collect radio waves emitted by celestial bodies and convert them into
electrical signals, which can be used to reproduce images. The Hubble telescope is an example of a reflecting telescope.
Robots Autonomous Explorers:
Robots Autonomous Explorers:
In 1997 NASA sent its Mars Rover Explorer, Mars Path Finder, to Mars to investigate the geology and morphology of that planet's surface, and hundreds of meters below ground, geochemistry and soil and petrology. of the rocks, the magnetic properties of the soil, such as the magnetic properties of dust.
Vehicle Explorer of the Moon:
The vehicle was first used on the Apollo 15 mission and was the fourth landing of the Apollo mission on the moon. The vehicle was used to explore distant regions about 5 km from the landing site. The vehicle was also used on the Apollo 16 and Apollo 17 missions.
Observatories:
Within an astronomical observatory, the astronomer conducts his research in several areas of Astronomy, if we observe a star for example with other equipment such as the spectroscope, we can know its distance from us, we can know its chemical composition, its temperature, its flow of light, among others.
Space Observatories: A Space Observatory is any instrument in outer space, used for astronomical observation. Astronomical observatories include astronomical satellites, which remain in orbit around the Earth or around other planets, and interplanetary probes sent to study distant planets, comets, asteroids, and so on.
Interplanetary Probes: A space probe is an unmanned spacecraft used for remote exploration of other planets, satellites, asteroids, or comets. Normally the probes have telemetry capabilities, which allow you to study your physicochemical characteristics from a distance, taking pictures and sometimes also your environment. Some probes, such as Landers or Rovers, land on the surface of celestial bodies, for studies of their geology and climate. The first probes to study other stars were launched in the late 1950s by the defunct Soviet Union and the United States, early in space exploration, and that helped greatly to unravel the mysteries of the Universe. Recently, the European Union, Japan, China and India have also launched their probes. A space rocket usually has the objective of sending objects (especially artificial satellites and space probes) and / or special spacecraft and men into space. A rocket consists of a structure, a propulsion motor and a payload. The structure serves to house the fuel and oxidant tanks (oxidizer) and the payload. It is also called "rocket" to the propulsion engine only.
Space Shuttle:
A space shuttle is the partially reusable vehicle used by NASA as a launch vehicle and spacecraft for its manned missions. He became the successor to the Apollo spacecraft used during the Apollo Project. The
bus flew for the first time in 1981. To get across the Earth's
atmosphere, the space shuttle is coupled to a rocket (note in the image
above).















0 Comments